Sensor-Based Multi-Robot Coverage with Spatial Separation
Cooperative exploration policy that keeps heterogeneous robots coordinated and collision-free.
Mission
We study how to allocate sensing tasks across aerial and ground robots operating in cluttered, unknown environments without human supervision (Wang et al., 2024). The goal is to maintain persistent coverage while guaranteeing that teammates do not violate separation constraints that protect onboard sensors and delicate payloads.
What’s New
- Sensor-aware decomposition: Partition the environment using real-time signed distance fields so each robot receives regions matching its sensing footprint.
- Spatial separation controller: Layer control barrier functions on top of nominal coverage controllers to ensure agents never approach closer than a configurable safety margin.
- Adaptive workload balancing: Adjust task assignments online based on local observability and remaining frontiers, which keeps coverage uniform even as robots fail or environments change.
Field Pipeline

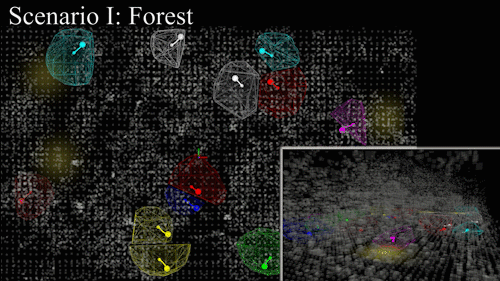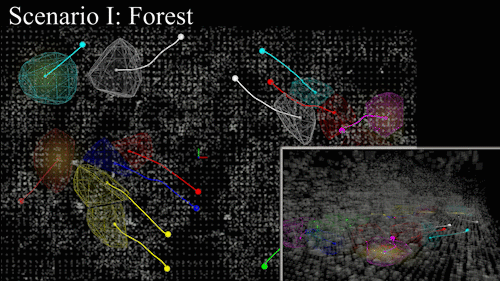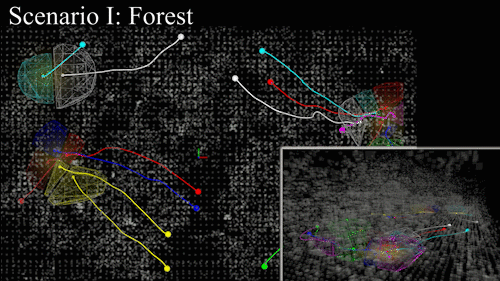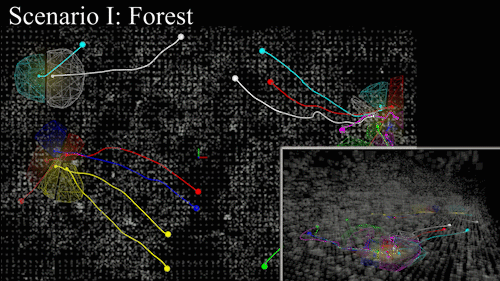
Perception-to-control loop deployed on aerial and ground platforms. Spatial separation constraints activate automatically when robots converge on the same frontier.

Hardware-in-the-loop experiments in an unstructured forest track improved coverage efficiency by 21% over prior decentralized approaches while respecting safety envelopes.
Resources
- Conference talk: ICRA 2024 presentation slides and recording (request access).
- Paper (PDF): Sensor-based Multi-Robot Coverage Control with Spatial Separation in Unstructured Environments
- Preview clips: Available on the project’s media drive; contact us for high-resolution footage.
Interested in trying the controller on your platform? Reach out for ROS 2 launch files and gazebo benchmarks. A public code release is scheduled alongside our journal extension.